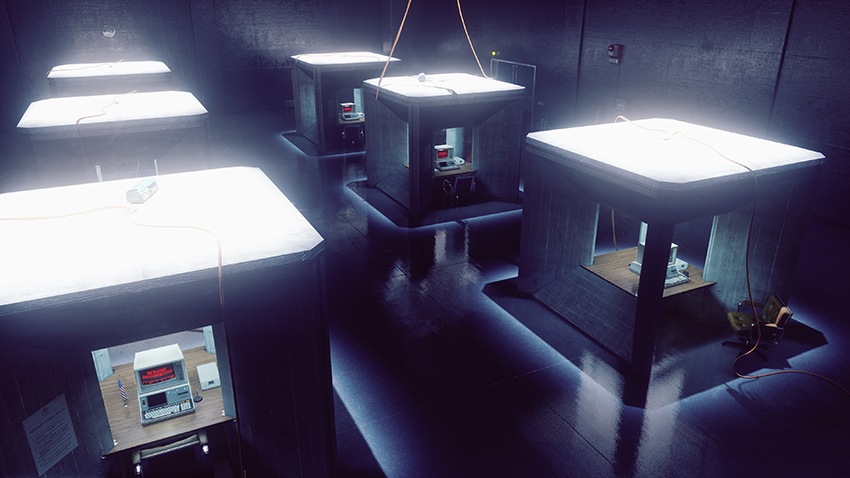
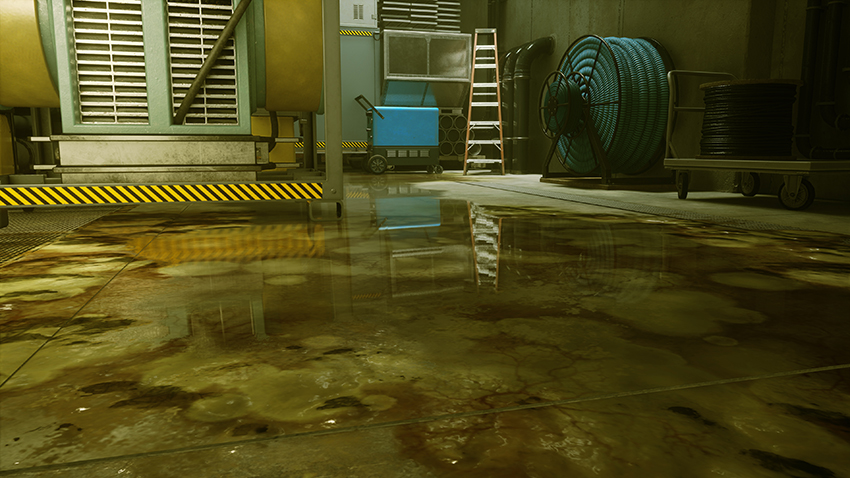
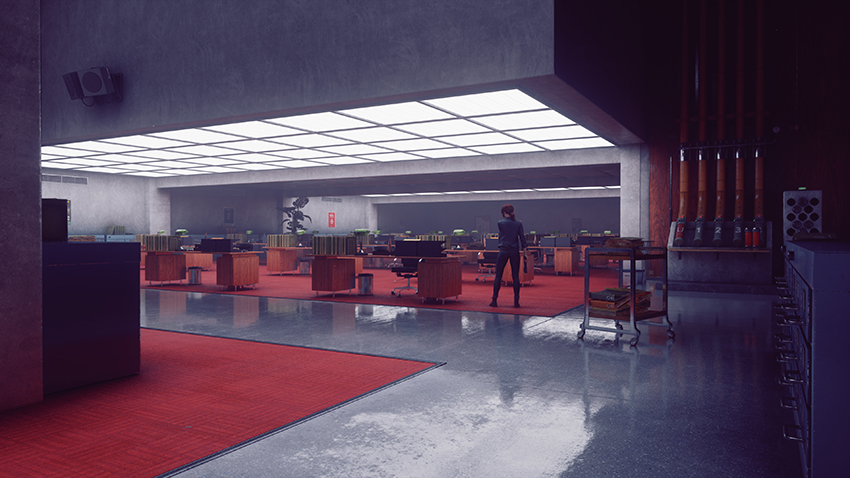
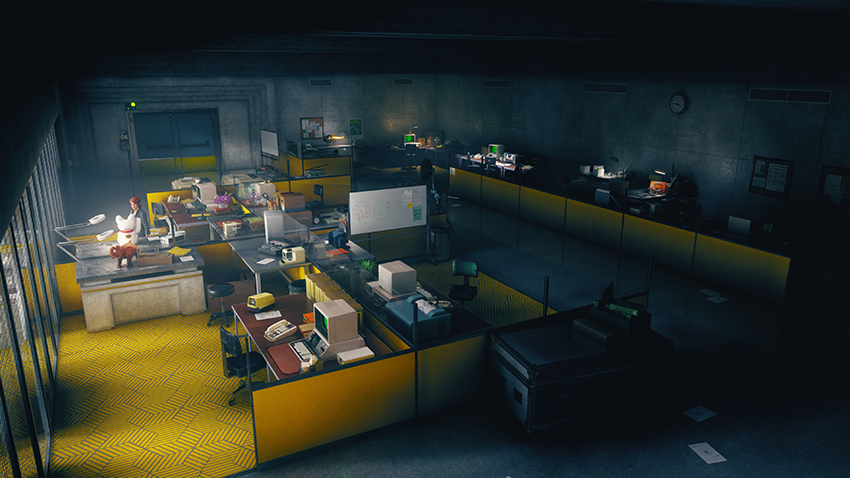
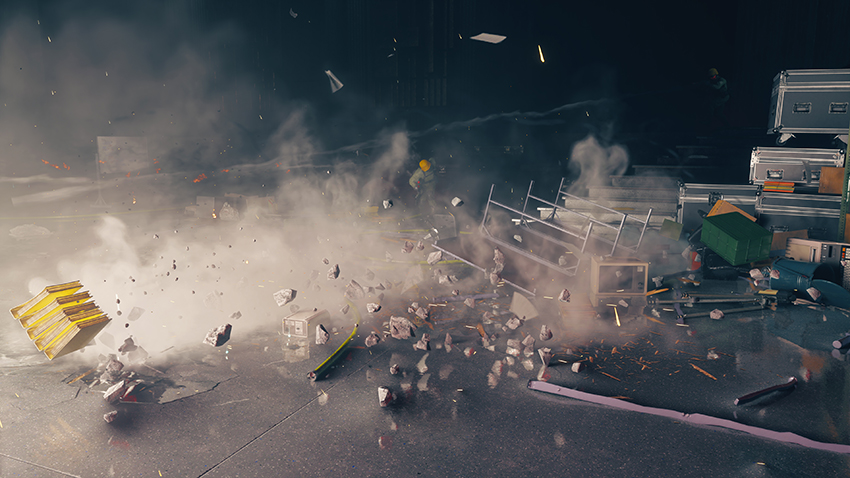Control Graphics and Performance Guide: Get The Inside Track On Ray-Traced Effects, DLSS and Every Other Aspect of The Critically-Acclaimed Game
Remedy Entertainment has a long history of crafting narratively led, cinematic action games, starting with their 2001 classic, Max Payne. Now, in partnership with 505 Games, Remedy is releasing Control, a third-person supernatural action shooter set in the Federal Bureau of Control.
Ordinarily, the FBC protect the U.S. populace from things that go bump in the night, whilst also covering up their existence, but recently the supernatural has invaded the Oldest House, the FBC's paranormal New York headquarters.
Players investigating the commotion at the FBC take control of Jesse Faden, who just happens to arrive at the Oldest House when it all goes a bit... wrong. Explore, fight, and use abilities to give you an edge. And if you’re the type of gamer who loves to explore every nook and cranny, there’s plenty of Metroidvania-style secrets to discover and exploit as your arsenal expands.
For Control, Remedy has rolled out a new iteration of their Northlight Engine, first seen in the transmedia-enhanced Quantum Break, which marked a new chapter in Remedy’s search for a filmic, cinematic look. Accordingly, Control is super-realistic, with soft, yet detailed visuals, that on PC are upgraded with several lifelike ray-traced effects that take graphical fidelity to new heights.
These five ray-traced effects enhance shadows, reflections, lighting, and more, and when enabled simultaneously complement and improve one another, enhancing every moment of your time in Control.
Dark hallways are illuminated by reflected ray-traced light. Light is colored by objects and diffused naturally. Transparent and opaque surfaces feature realistic real-time reflections. Shadowing is improved. And combat appears more dynamic, with all ray-traced effects applied to fractured marble, broken wood, and other destructible objects.
So get comfy, and prepare to delve into Control's PC settings and ray-traced effects, with examinations of each using interactive comparison screenshots, relative performance charts, and written explainers, giving you all the info you need to tweak and tailor your graphics and performance.
Guide Contents:
- NVIDIA RTX Ray Tracing
- System Requirements
- Control Bundle
- Graphics Settings
- Far Object Detail (LOD)
- Global Reflections
- Screen Space Reflections Quality (SSR)
- Ray-Traced Reflections
- Ray-Traced Transparent Reflections
- Shadow Resolution
- Shadow Filtering
- Ray-Traced Contact Shadows
- Ray-Traced Indirect Diffuse Lighting
- Screen Space Ambient Occlusion (SSAO)
- Ray-Traced Debris
- Texture Filtering
- Texture Resolution
- Volumetric Lighting
- NVIDIA DLSS, MSAA and Other Anti-Aliasing
- Ray Tracing Grand Finale
- Settings Wrap-Up
- GeForce Experience: Optimal Playable Settings With A Single Click
- Control Game Ready Driver
- Conclusion
NVIDIA RTX Ray Tracing, Available From Day-1
From the second you start playing Control, you'll have the option to enable five real-time ray-traced effects that greatly enhance image quality and immersion:
- Ray-Traced Reflections: Surrounding detail is reflected with unparalleled accuracy and fidelity
- Ray-Traced Transparent Reflections: In a world first, detail is dynamically reflected on transparent windows
- Ray-Traced Contact Shadows: Existing shadows are enhanced with lifelike detail, and entirely new shadows are rendered
- Ray-Traced Indirect Diffuse Lighting: Accurate real-time lighting enhances every scene, with diffuse light bouncing from nearby illuminated surfaces, causing subtle but realistic color bleeding
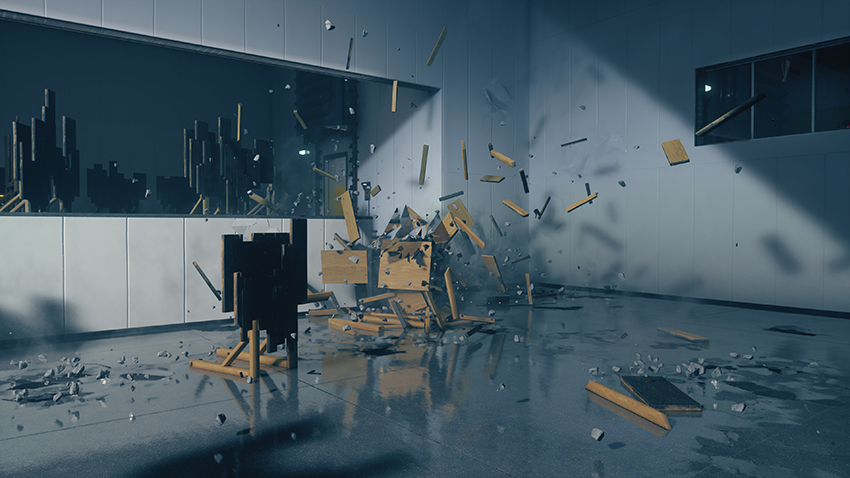
- Ray-Traced Debris: Destructible objects can enhance and can be enhanced by other ray-traced effects, further improving graphical fidelity
Any form of ray tracing improves image quality immensely, but by employing multiple ray-traced effects simultaneously, nearly everything gains lifelike realism. And when your movements, attacks and actions are constantly affecting the appearance of the world around you, you feel more connected to the gameplay, as if your actions are having a real impact.
In Control, much of the environment is destructible, and enemies abound, causing constant changes to lighting, shadowing and reflections. With ray tracing enabled, you'll experience a new benchmark in dynamic graphics, which simply couldn't be attained using traditional rasterized techniques.
For all the details, and to learn how ray-traced effects can affect other game settings, keep reading this comprehensive Control Graphics and Performance Guide.
Control System Requirements
To play Control with ray tracing enabled, Remedy is recommending players equip their systems with a GeForce RTX 2060, or better, 16GB of RAM, and an Intel Core i5-8600K, or AMD Ryzen 7 2700X CPU:
Time-Limited Control GeForce RTX Bundle
If you lack a recommended GeForce RTX graphics card, search retailers for our newest GPU, desktop and laptop bundle, which just happens to include a copy of Control, along with Wolfenstein: Youngblood, a recently-released first-person shooter that will soon be enhanced with ray tracing.
This SUPER FAST. SUPERNATURAL Bundle is available now with qualifying products until September 16th, 2019, at participating retailers around the world. Learn more here.
Control Graphics Settings
Control includes 17 settings, affecting image quality and performance, giving you plenty to configure and tweak in your quest for the definitive experience. For all the details, keep reading.
Far Object Detail (LOD)
In Control's office environments, draw distances never approach those of say, an open world game. As such, Control's Level of Detail option, Far Object Detail, often has little effect on a scene.
In our artificial test below, we've flown far from the game's heroine, who's in the process of destroying the scenery. Dropping from High, to Medium, only a few distant embellishments are culled, along with some shadowing and reflective shine. And up by the ceiling, the fidelity of foliage changes to no appreciable extent, though nearer the camera on the ground level a barrier does lose a literal chunk of detail.
On Low, however, wide scale changes are observed - the number of particle effects are reduced, foliage is removed, objects lose fine detail, and distant signs and other embellishments are entirely hidden.
| Interactive Comparisons | ||
| High vs. Medium | High vs. Low | Medium vs. Low |
Performance: Ultimately, removing a few bits and pieces affects performance by less than 2 frames per second, though it does noticeably reduce draw distances, while simultaneously increasing pop in and pop out. Because of this, we recommend you leave Far Object Detail maxed out unless you're desperate to improve framerates.

Global Reflections
Along with Screen Space Reflections, Ray-Traced Reflections, and Ray-Traced Transparent Reflections, Global Reflections affects the quality and visibility of Control's many reflections.
In the case of Global Reflections, the reflective specular shine seen on metals and other surface types is affected or entirely disabled, though for it to work Screen Space Reflections must also be on.
| Interactive Comparisons | ||
| High vs. Medium | High vs. Off | Medium vs. Off |
In the scene above, there's little to differentiate High and Medium, and Off looks OK'ish, though obviously less realistic. From a different angle, however, we can see just how significantly the scene is affected by the disabling of Global Reflections:
Returning to the question of High and Medium quality, we're switching scenes and placing our protagonist in front of a strongly illuminated scientific doodad, which is also showing her Screen Space Reflection.
By swiping between the two detail levels, we can see Medium's Global Reflection is blurry, and its visual intensity is reduced - traits repeated across the entirety of Control. And when we switch Global Reflections off, all metal loses its specular shine, greatly reducing realism and image quality.
| Interactive Comparisons | ||
| High vs. Medium | High vs. Off | Medium vs. Off |
Finally, let's chat about ray tracing. If you watched our Tech Explainer near the beginning of the guide, you'll know that we trace rays a finite distance across a scene - a logical approach that maximizes the visual benefit, enhancing prominent game elements, while keeping ray-traced effects performant. If there should be visible detail beyond a ray's reach, we blend the game’s pre-baked volumetric global illumination with ray tracing, resulting in high-performance hybrid ray-traced gameplay.
With regards to Global Reflections, Ray-Traced Reflections almost entirely replace the effect's approximated specular shine and reflected detail with fully ray-traced, highly accurate reflections. Image quality is bolstered to a considerable degree, and shiny, metallic surfaces and objects are fully reflected on glossy floors and other reflective surfaces.
Performance: In most instances, only a few frames per second separate High and Medium Global Reflections, though when switched off it does deliver a big boost, albeit at a heavy cost to image quality.

Screen Space Reflections Quality (SSR)
Screen Space Reflection techniques attempt to mirror what's currently on-screen on reflective surfaces. In Control, High and Medium detail levels are on offer, along with a toggle that will disable the setting (as already discussed, switching-off SSR also turns off Global Reflections, which requires SSR to function).
So, what's the difference between High and Medium? Quite simply, the fidelity of the reflection. On High, SSR is pushed to the limit, rendering its reflections with excellent clarity and temporal stability (their quality when the player or camera is moving). On Medium, quality is severely reduced, decreasing reflection visibility, accuracy and temporal stability, as demonstrated below.
| Interactive Comparisons | ||
| High vs. Medium | High vs. Off | Medium vs. Off |
This reduction in detail is found on every reflection, and the speckling prominently shown in our first set of comparisons can also be seen on other surfaces and surface types, too.
| Interactive Comparisons | ||
| High vs. Medium | High vs. Off | Medium vs. Off |
Performance: The upside of Medium is the sizable speed-up it brings, increasing performance by 8-13 frames per second in the half dozen areas we benchmarked. And as Medium only runs 2-3 frames per second slower than Off, even low performance PCs can enjoy some degree of reflectivity, greatly improving image quality throughout the game.

Ray-Traced Reflections
Much of our world is to some degree reflective. Look around you right now - aged hardwood floors reflect light and show coarse object reflections; rough white walls reflect light; and pretty much anything that isn’t matte black to some extent reflects light and/or detail. But without this subtle reflectivity, which we observe every waking minute of every day, immersion and realism in games is greatly reduced.
With ray tracing we can fix this, because unlike screen space techniques that can only reflect what’s on screen, ray-traced reflections incorporate the entire scene around the character and camera, and can accurately represent objects outside and facing away from the camera's view. This enables 360 degrees of reflectivity, as well the reflection of off-screen and occluded detail. And because rays reach most game elements, virtually everything can receive reflections or be reflected onto other objects and surfaces, creating lifelike scenes that were previously impossible to render.
In Control, Ray-Traced Reflections override Screen Space Reflections to deliver this experience.
Beyond geometry, lighting, shadows and visual effects can also be reflected, leading to the creation of accurate shadowing around objects, more realistic lighting on surfaces, and more dynamic combat encounters. And of course, each improvement is rendered and updated in real time, so as the environment changes so do the effects.
And yes, wet floors do gain unprecedented reflective detail, with pixel-perfect recreations, each adhering to the Fresnel Effect’s reflection equations. Surfaces such as these are the showcase reflection effect in any game, and at the time of writing Control’s are the best in the business.
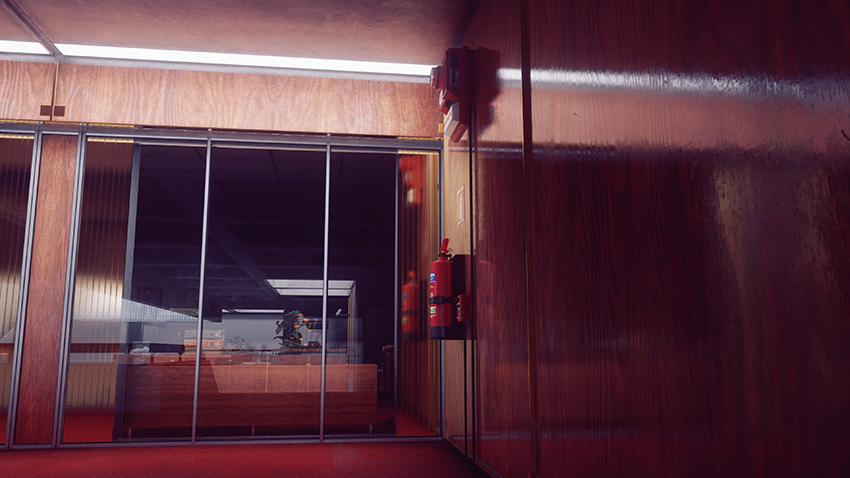
Below, you can see a clear example of Screen Space Reflections being unable to accurately render a scene - as it can only reflect what the player sees on-screen, the visible portion of the fire extinguisher and alarm is reflected across the opaque surface. In comparison, ray tracing reflects the hidden side, while also improving reflectivity on the wooden wall.
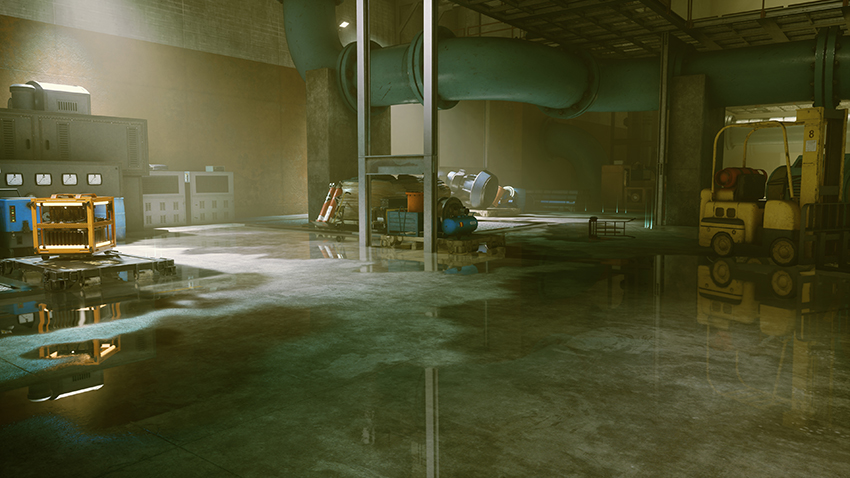
In industrial and scientific areas of Control's Federal Bureau of Control, glossy floors, machinery and ducting are transformed, gaining accurate real-time reflections that reflect all surrounding detail:
Close up, because Screen Space Reflections can't see the display's illumination, it isn't reflected on-screen, affecting the quality of the scene.
During gameplay, you'll frequently find illumination behind and out of view of the camera, and with ray tracing this will reflected around the environment, for a far more immersive experience.
And finally, just for fun, here's an extreme close-up of a Bureau soldier and the ray-traced reflections that are added to his gear (at normal gameplay distances, these are yet another example of subtle, extra reflections that improve realism and immersion):
Performance: Regardless of the game, ray tracing performance is affected by three things:
- Screen Resolution: Higher resolutions use more pixels, and at least one ray needs to be sent to every pixel every frame to enable real-time ray tracing. Compared to a 1920x1080 monitor, a 2560x1440 display has 77% more pixels, so ray tracing at higher resolutions will be significantly more demanding
- RT Cores: GeForce RTX GPUs have RT Cores, physical hardware designed to accelerate ray tracing workloads. Each GPU has a different amount of RT Cores, and the more you have the faster your ray tracing performance will be
- Content On-Screen: Ray-traced programming has evolved to the point where we know what's in a scene, and what's likely to benefit from ray tracing. As such, one cannot put a hard number on the framerate cost of a specific ray-traced effect, as its use and application will vary from location to location. For our benchmarks, we test the most intensive locations to show the maximum cost of an effect, meaning in many instances performance will be higher than shown in this guide
With all of the above in mind, here's how Ray-Traced Reflections measured-up when we looked sideways across the room shown in this earlier example:
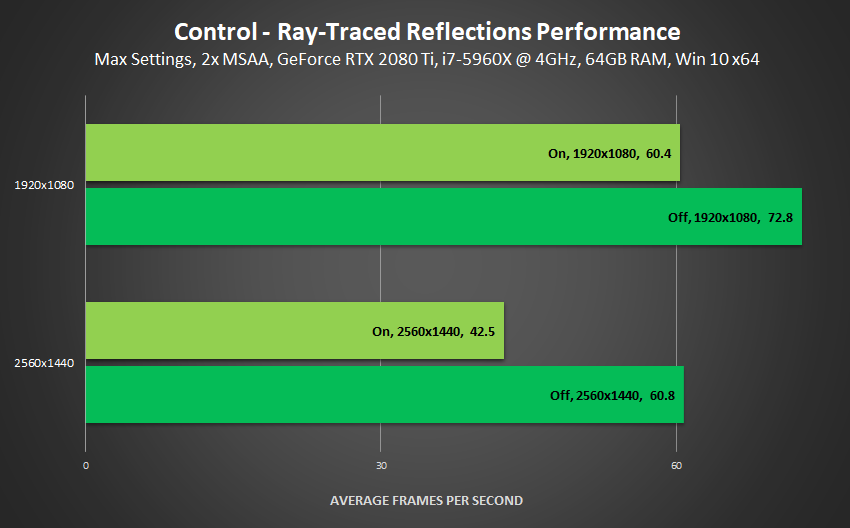
Bear in mind, Screen Space Reflections cost 11 frames per second on High, and the supplementary Global Reflections cost 17 frames per second to enable in areas with reflective metals. So, when you consider their combined cost, and the fact that Ray-Traced Reflections is doing 99% of their work at a far higher level of detail, and applying that work to far more of each scene, the performance of Ray-Traced Reflections is in fact comparatively low.
Ray-Traced Transparent Reflections
Adding ray-traced reflections to glass is no different than ray tracing a puddle, if the background is opaque. When it’s transparent, with detail visible on the other side, extra work is required.
The newly-created Ray-Traced Transparent Reflections solves the problem, tracing rays from transparent surfaces to surrounding detail, enabling realistic mirror-like reflectivity without blocking the visibility of detail beyond the transparent surface.
In the comparison below, we see Control’s generalized cubemap reflections replaced with real-time transparent reflections capable of showing characters, NPCs and other dynamic game elements moving across the scene. And as an added extra, we've enabled fractured glass to naturally display these transparent reflections.
The Federal Bureau of Control is chock-full of offices and windows that make full use of this technology, and once you experience it, it’s impossible to return to the cubemaps of old.
Performance: Ray-Traced Transparent Reflections' high-fidelity additions are the most noticeable ray-traced addition, adorning numerous offices and windows in the early stages of Control, decreasing our performance by a maximum of 21%.
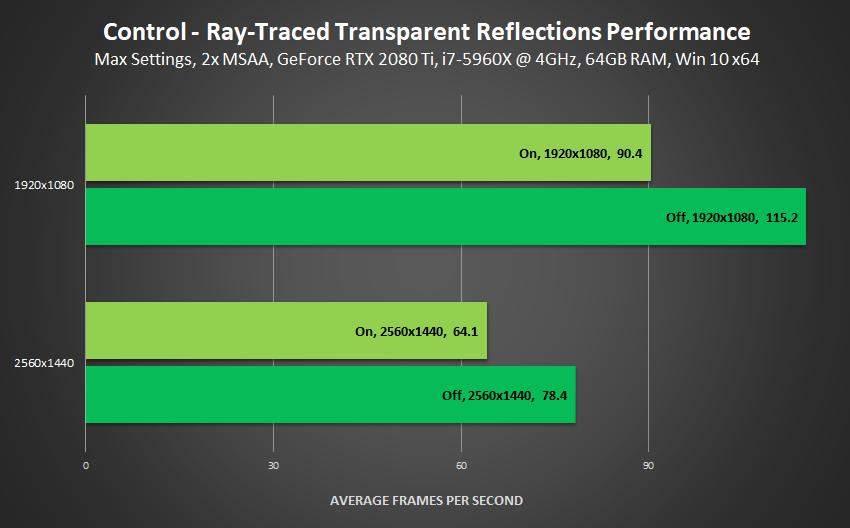
If forced to choose a single ray-traced effect, I'd select Ray-Traced Transparent Reflections, as without them every window and transparent surface has a generalized cubemap that looks out of place in Control's high fidelity, realistic world. Other ray-traced effects offer substantial enhancements and improvements, but only Ray-Traced Transparent Reflections introduces an entirely new feature that's seen time and again throughout the entirety of the game.
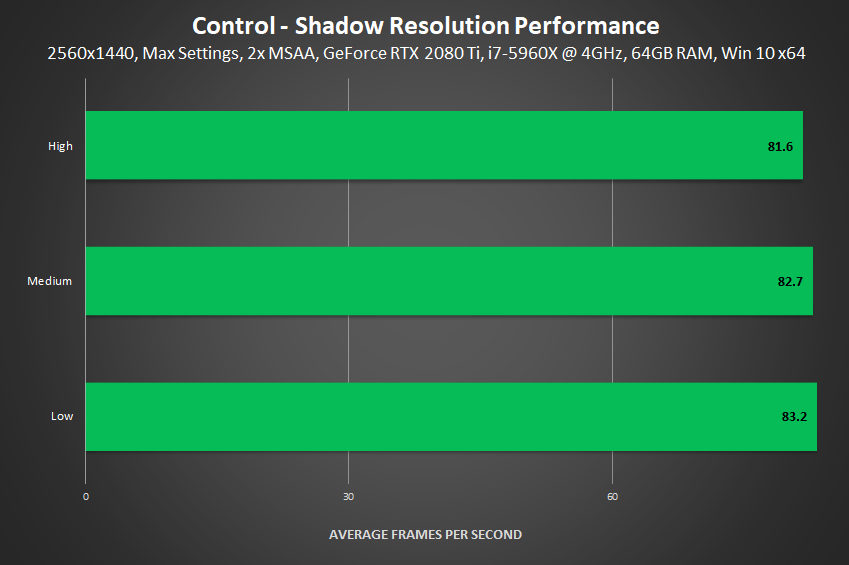
Shadow Resolution
Rasterized Shadow Maps bring Control's shadows to life, enhancing innumerable scenes with long, stretching shadows, and other stylistic light-shadow setups that look great.
As with other settings, Low, Medium and High are the available detail levels. And from our testing, we've found that going from Low to Medium improves the quality of shadows on small game elements, like the chair shown in a later comparison, and moving from Medium to High improves larger shadows or those that are displayed far from the shadow caster.
Below, you can observe the improvement to shadow fidelity from High's higher-resolution shadow maps:
| Interactive Comparisons | ||
| High vs. Medium | High vs. Low | Medium vs. Low |
From t'other end of the scene, we can see improvements to shadow quality and visibility on railings and stairs, along with a few other changes here and there:
| Interactive Comparisons | ||
| High vs. Medium | High vs. Low | Medium vs. Low |
Up close, with the aforementioned chair, the benefits of stepping up from Low to Medium are immediately evident:
| Interactive Comparisons | ||
| High vs. Medium | High vs. Low | Medium vs. Low |
Performance: Typically, shadow maps have a moderate performance cost. However, in Control, we found little difference between detail levels at any resolution, in any location, and even with a different GPU. We will therefore be revisiting this testing with the public version of the game once available, just in case something's amiss.
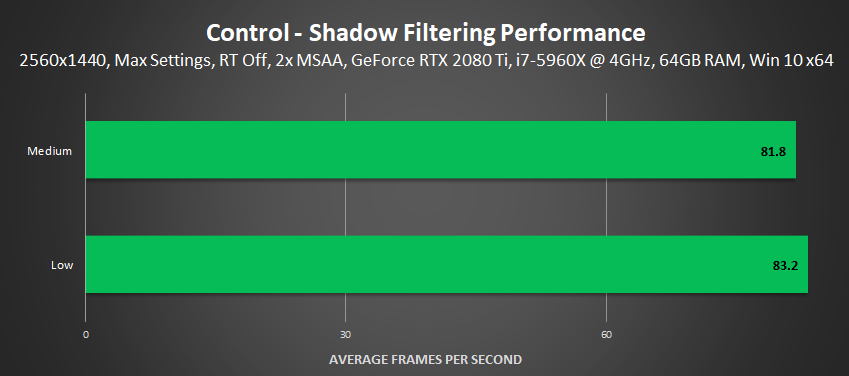
Shadow Filtering
To reduce aliasing on shadow edges, and to improve temporal stability when the shadow or game camera is moving, you can select Medium Shadow Filtering. In the comparison below, there's limited visual benefit, but in-game these thin shadows look significantly better and are far less aliased and flickery when the camera moves.
Performance: Making shadows look that bit better costs less than 2 frames per second.
Ray-Traced Contact Shadows
As discussed, Control’s shadows are formed with rasterized Shadow Maps, which serve its angular, functional offices rather well. When it comes to fine detail, however, they struggle – small and thin geometry is shown at low resolutions or omitted altogether, and objects far from the shadow caster may be barely perceptible.
If you’ve played plenty of games, you’ll know these are common issues caused by shadow mapping’s limitations, and by the necessity for developers to manually balance visibility and quality of shadows against the associated performance and video memory costs.
By enabling Ray-Traced Contact Shadows, we can give the shadow maps a helping hand, tracing rays to light sources to create accurate real-time shadows that improve what’s already there, and to render the detail they couldn’t.
| Interactive Comparisons | ||
| All RT Effects On vs. RT Contact Shadows | All RT Effects On vs. Off | RT Contact Shadows On vs. Off |
Our comparison above perfectly demonstrates the benefits of ray-traced shadowing: contact hardening shadows with realistic penumbras are cast from each chair; additional shadows are cast around our heroine’s feet, grounding her to the scene; office furniture gains soft shadows; and additional shadows are cast on and around clothes, objects and other game elements.
These naturally and effortlessly enhance shadow maps, ensuring each scene’s realism is improved.
Later, players reach industrial areas deep beneath the shiny, reflective offices. Here, machinery and chain link fences gain shadowing that is otherwise entirely absent.
| Interactive Comparisons | ||
| All RT Effects On vs. RT Contact Shadows | All RT Effects On vs. Off | RT Contact Shadows On vs. Off |
When the rockets start flying, ray-traced contact shadows can be dynamically drawn as the light-emitting missiles pass through the scene, giving you an extra level of visual refinement.
| Interactive Comparisons | ||
| All RT Effects On vs. RT Contact Shadows | All RT Effects On vs. Off | RT Contact Shadows On vs. Off |
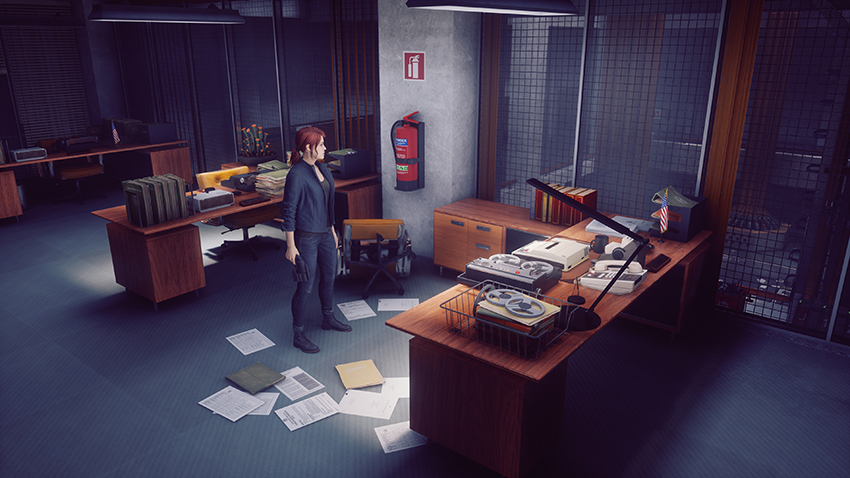
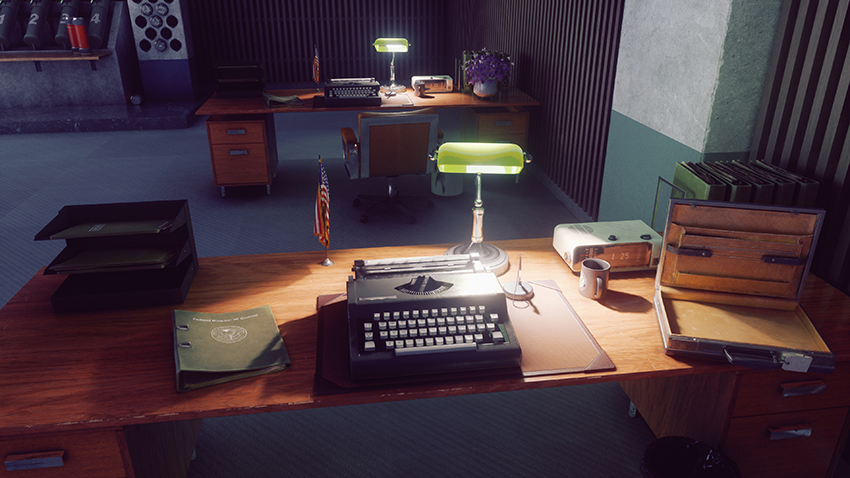
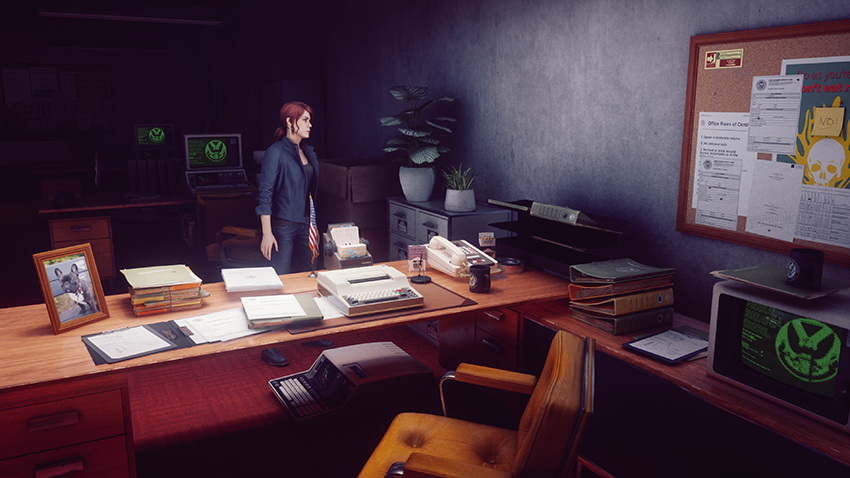
Control's many offices see their stacks of paper, typewriters, computers, binders, and other objects enhanced with new, realistic shadows:
| Interactive Comparisons | ||
| All RT Effects On vs. RT Contact Shadows | All RT Effects On vs. Off | RT Contact Shadows On vs. Off |
And our protagonist's super cool leather jacket gets some extra ray-traced TLC, bringing us one step closer to creating a ray-traced CG Jensen:
| Interactive Comparisons | ||
| All RT Effects On vs. RT Contact Shadows | All RT Effects On vs. Off | RT Contact Shadows On vs. Off |
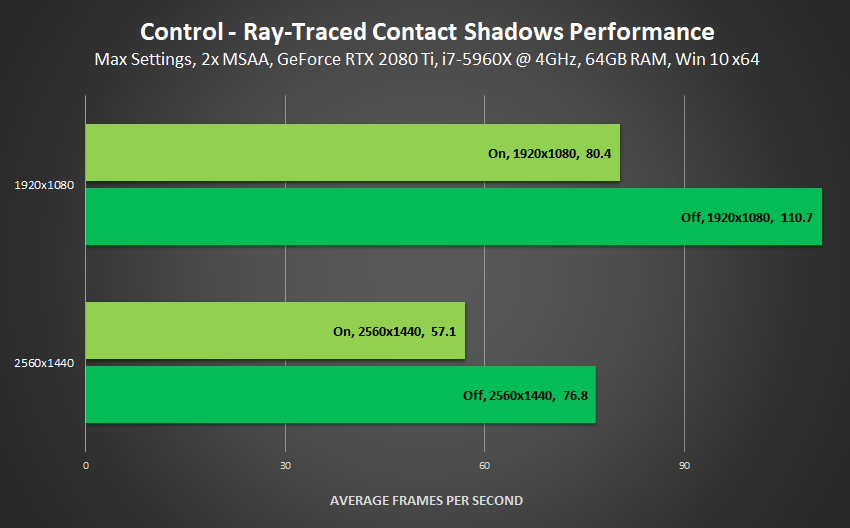
Performance: Ray-Traced Contact Shadows add an additional level of refinement to Control, grounding objects, enhancing existing shadows, and drawing accurate new shadows, with contact hardening and realistic penumbras. To add them to your copy of Control, they'll require up to 27% of your frames in graphically-advanced areas, though in the majority of instances it's more like 15-20%.
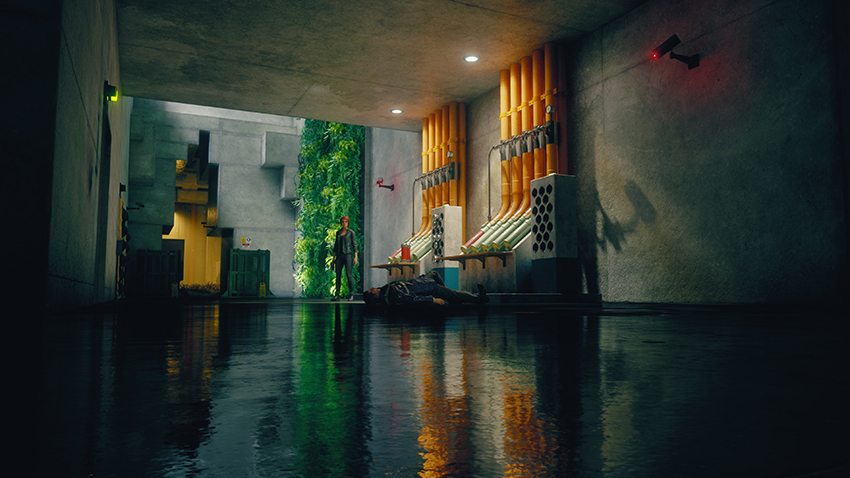
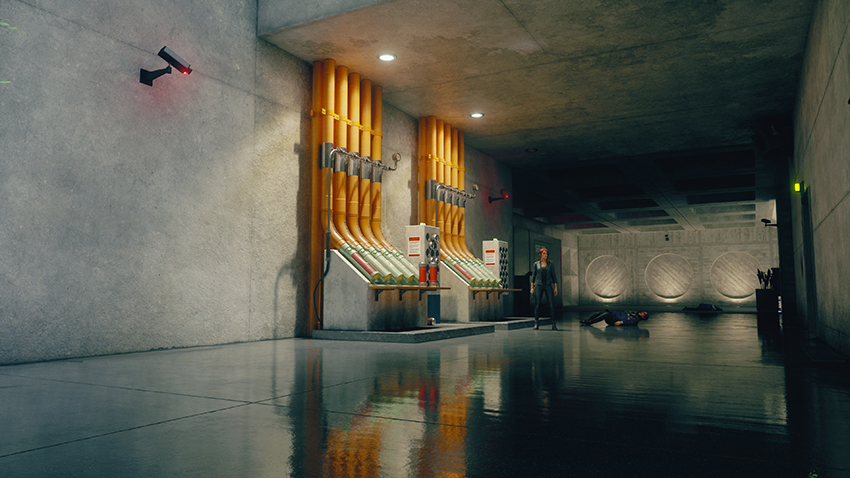
Ray-Traced Indirect Diffuse Lighting
Control is illuminated with a mixture of lighting techniques, including precomputed global illumination. To add some extra pizzazz to proceedings, players can enable Ray-Traced Indirect Diffuse Lighting, which in simpler terms means that rays are traced, and if a ray strikes a bright light or surface, surrounding game elements will be naturally illuminated.
In addition, if the ray’s point of contact happens to be colored, that color will naturally spread to surrounding detail.
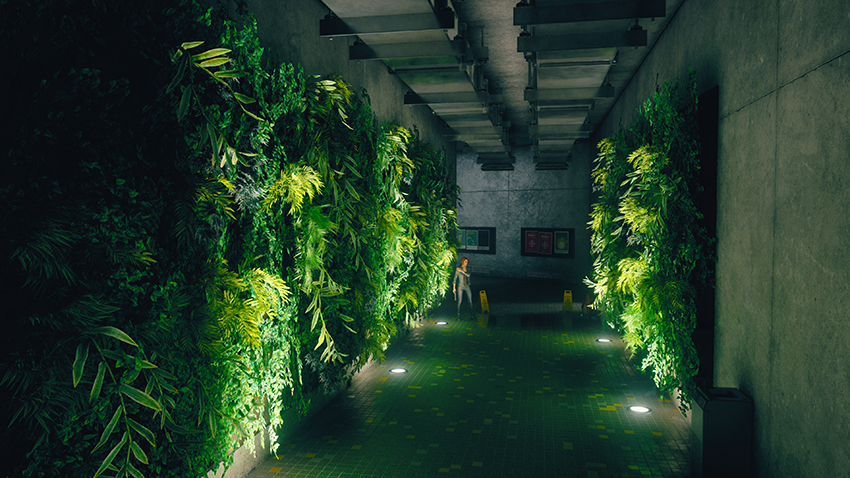
For an example, check out the interactive comparison below. Without ray tracing, a bright white spotlight simply illuminates green foliage. But with ray tracing, the bright light realistically bounces from the foliage, absorbing its color, naturally bathing the floor, walls, and deeper layers of foliage with green light.
| Interactive Comparisons | ||
| All RT Effects On vs. RT Lighting | All RT Effects On vs. Off | RT Lighting On vs. Off |
In the example below, diffuse orange light spreads across the nearby ceiling and the pneumatic tubes themselves, and other lighting and shadowing near walls and geometry improves. But further away for the walls, existing GI is used for lighting, hence the lack of change.
| Interactive Comparisons | ||
| All RT Effects On vs. RT Lighting | All RT Effects On vs. Off | RT Lighting On vs. Off |
From an alternative angle, we can see superior contact shadowing, the front layer of pipes casting accurate shadows on the back line, plus numerous other improvements. And of course, all these improvements stack with other ray-traced effects, further enhancing image quality, immersion, and realism.
| Interactive Comparisons | ||
| All RT Effects On vs. RT Lighting | All RT Effects On vs. Off | RT Lighting On vs. Off |
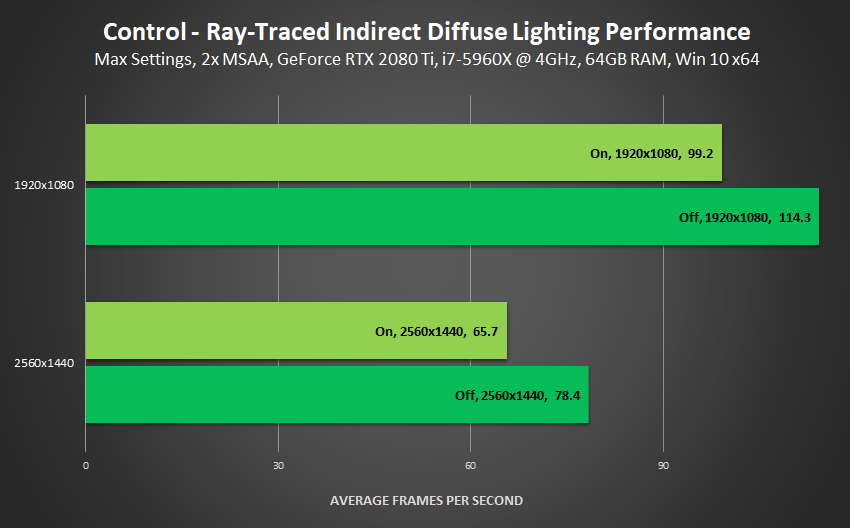
Performance: Ray-Traced Indirect Diffuse Lighting's realistic real-time global illumination effects were between 13 and 16% slower in most locations we visited.
Screen Space Ambient Occlusion (SSAO)
SSAO adds approximated contact shadows where two objects meet, and where objects occlude light. In other words, SSAO adds extra shadows in locations other rasterized shadow effects couldn't account for, such as around object bases, in the thin gaps between a table and wall, and in corners where two walls meet.
In Control, if you have ray tracing disabled, SSAO will introduce much-needed contact shadowing, improving image quality and realism:
| Interactive Comparisons | ||
| On vs. Off | SSAO On, RT On vs. SSAO Off, RT On | |
If you do have Ray Tracing enabled, SSAO can still affect some scenes, though to a very limited extent:
| Interactive Comparisons | ||
| On vs. Off | SSAO On, RT On vs. SSAO Off, RT On | |
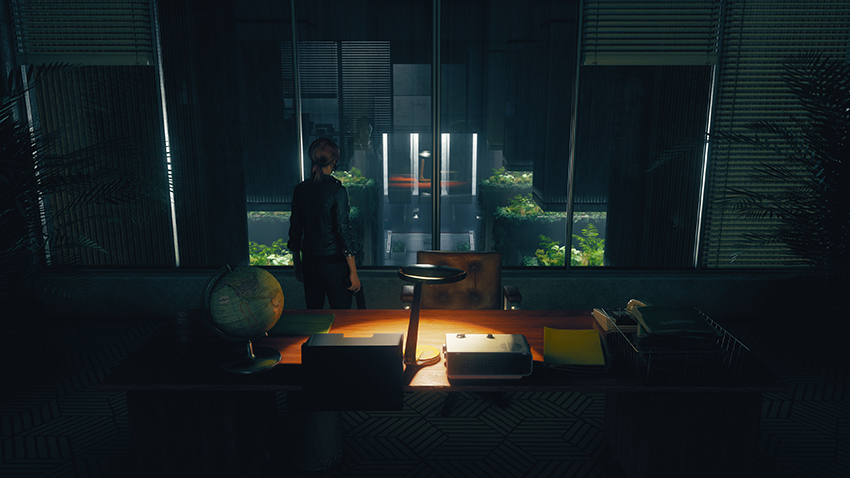
However, I personally prefer to disable SSAO when ray tracing is enabled, as I find it over darkens affected areas. For instance, in the comparison below, the lamps are intended to cast very bright light across each desk. But with SSAO on, that effect is dulled. And the final nail in the coffin: incorrect contact shadowing is observed on the rings of the binder.
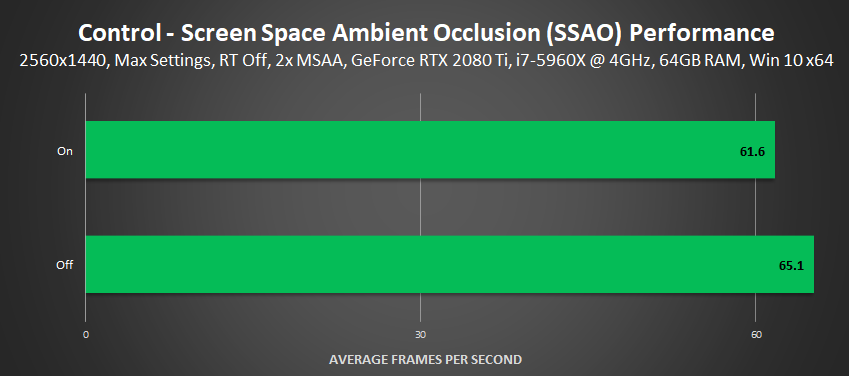
Performance: Control's Screen Space Ambient Occlusion effects costs 4-5 FPS when ray tracing is off, and about 1-3 FPS when it is on.
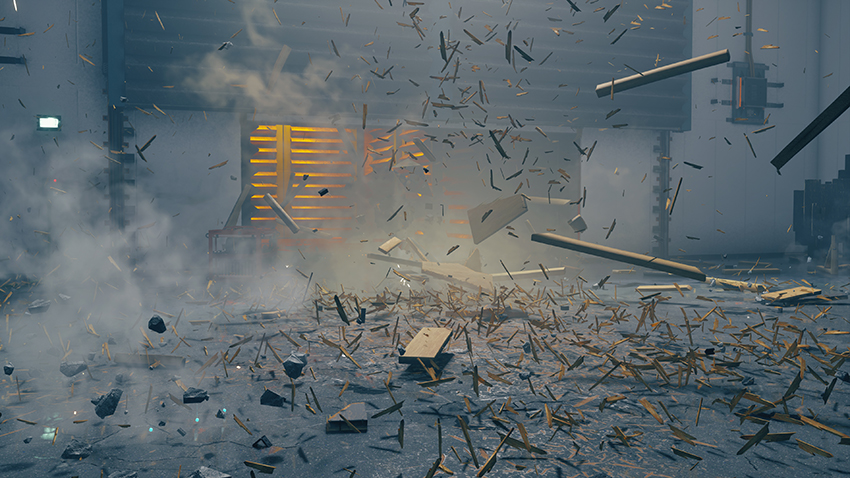
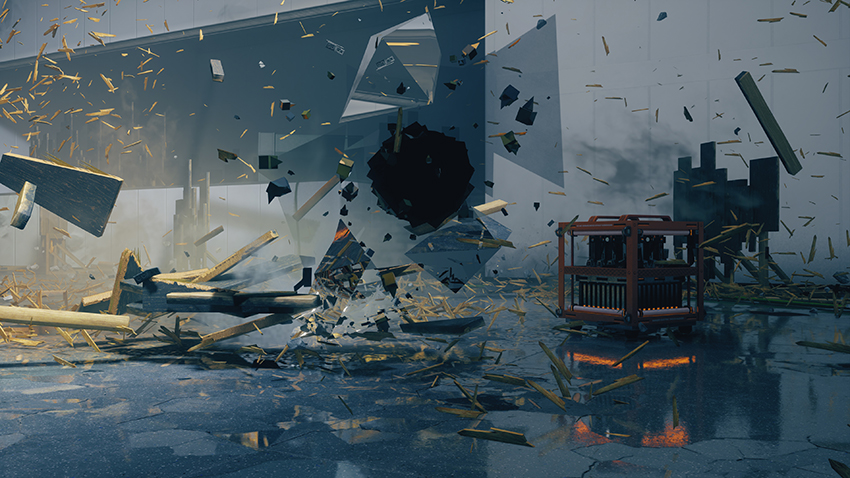
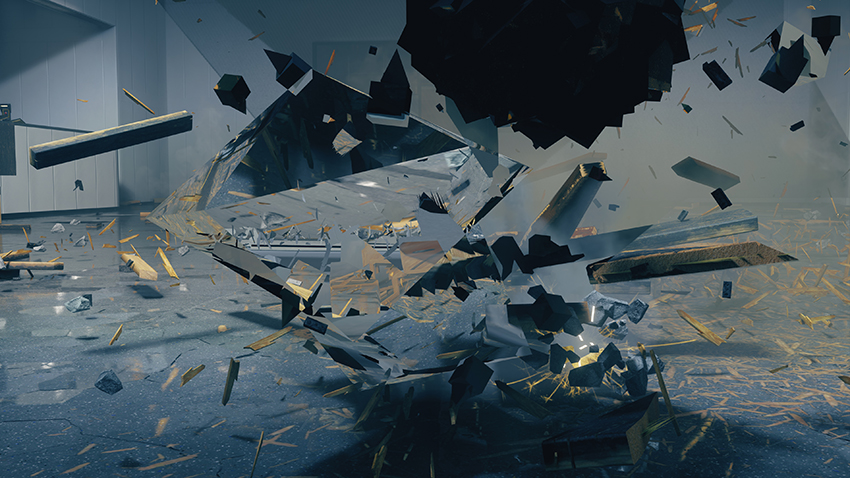
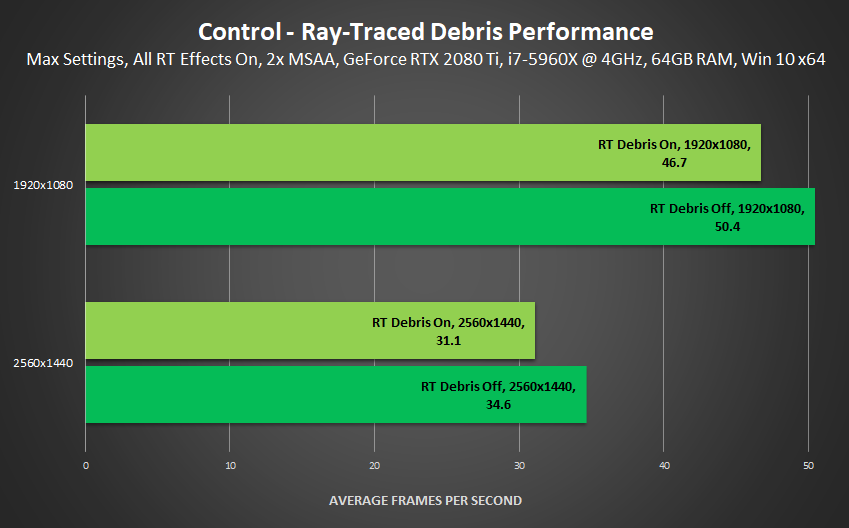
Ray-Traced Debris
As you fight your way through the Federal Bureau of Control, it's scenery and objects will take a beating, temporarily filling the vicinity with debris. If a ray tracing effect is enabled, and you switch on Ray-Traced Debris, that effect will also be applied to the debris.
Ray-Traced Reflections enables debris to be reflected on surfaces, and for glossy debris to reflect surrounding detail; Ray-Traced Contact Shadows adds detailed shadows to debris and enables them to cast their own shadows; and Ray-Traced Indirect Diffuse Lighting applies appropriate lighting to debris, as well as letting debris affect the lighting of the scene.
| Interactive Comparisons | ||
| All RT Effects On vs. All Off | All RT Effects On vs. RT On, Debris Off | RT On, RT Debris Off vs. All RT Off |
This seemingly minor enhancement quickly becomes a scene stealer once you encounter an otherworldly enemy that destroys everything in its path:
| Interactive Comparisons | ||
| All RT Effects On vs. All Off | All RT Effects On vs. RT On, Debris Off | RT On, RT Debris Off vs. All RT Off |
With debris shadowed and reflected, it gains extra presence within the scene. And by enabling it to affect lighting, image quality is refined once more, taking us a step closer to photo realistic visuals.
| Interactive Comparisons | ||
| All RT Effects On vs. All Off | All RT Effects On vs. RT On, Debris Off | RT On, RT Debris Off vs. All RT Off |
Note how Ray-Traced Debris is enhanced by the other ray-traced effects, before be reflected by the enemy's glassy... stuff.
| Interactive Comparisons | ||
| All RT Effects On vs. All Off | All RT Effects On vs. RT On, Debris Off | RT On, RT Debris Off vs. All RT Off |
Ray-Traced Debris applies a final layer of refinement, helping connect the debris to the action by giving it physical properties that affect the rest of the scene in real-time. It's steps like these that will cumulatively give us movie-like pixel-perfect screen-wide ray tracing in the years to come.
| Interactive Comparisons | ||
| All RT Effects On vs. All Off | All RT Effects On vs. RT On, Debris Off | RT On, RT Debris Off vs. All RT Off |
Performance: Making combat more dynamic and visually striking reduced FPS by a max of 10% in an incredibly demanding firefight where we intentionally pushed the engine and destruction to the absolute limits, filling the scene with alpha effects and debris. In normal gameplay scenarios, expect a substantially higher framerate, and a typical Debris cost of around 5-7%.
Texture Filtering
Control's take on Anisotropic Filtering has only a minor impact on texture fidelity in the scenes we tested (look to the center of the screen on the specular shine):
| Interactive Comparisons | ||
| High vs. Medium | High vs. Low | Medium vs. Low |
Performance: Like most implementations of Anisotropic Filtering, Control's Texture Filtering has a minute cost, so as always, we recommend keeping it maxed out at all resolutions.

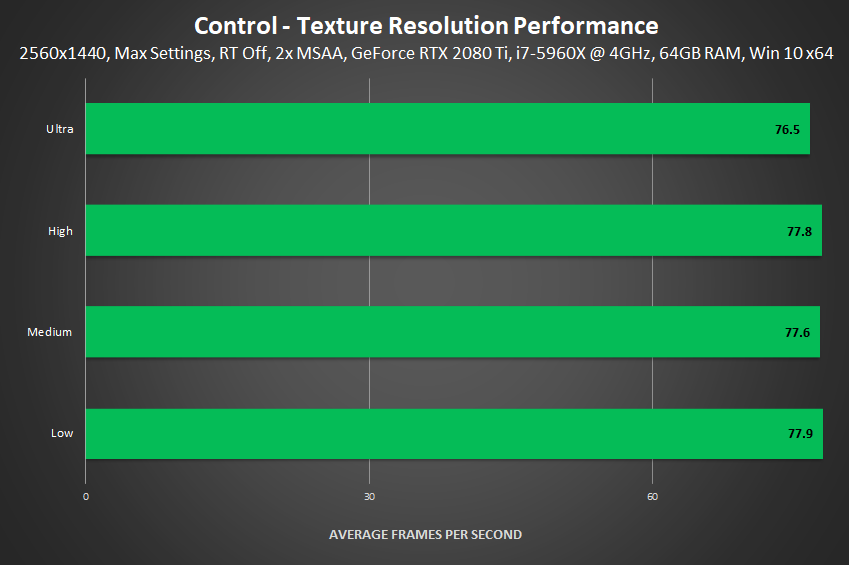
Texture Resolution
Control's Texture Resolution setting requires a full game restart to properly test, limiting us to respawn locations in just a few locations. Because of this, our comparisons are less useful than usual, but we'll share our observations below.
| Interactive Comparisons | ||
| Ultra vs. High | Ultra vs. Medium | Ultra vs. Low |
| High vs. Medium | High vs. Low | Medium vs. Low |
If you scour the comparisons above, you're unlikely to identify many differences, a trend that continues throughout the game. From what we saw, Low --> Medium improves floor and wall textures, and Medium --> High further improves them. High also improves textures on some objects, as well as on posters and documents found throughout the Federal Bureau of Control. And finally, Ultra appears to solely improve the fidelity of select textures at longer view distances, enabling you to read a poster's text from further away, for example.
| Interactive Comparisons | ||
| Ultra vs. High | Ultra vs. Medium | Ultra vs. Low |
| High vs. Medium | High vs. Low | Medium vs. Low |
No guidance is offered in-game on the amount of VRAM required for each detail level, and monitoring tools show the game simply caching in VRAM, so our only suggestion is set Texture Resolution to Ultra if you have a modern GPU, and if you notice textures taking a long time to stream in, drop to High.
Performance: The performance of Low, Medium and High is essentially the same. On Ultra, we suspect there's a few extra mipmaps in use for the better distant texture detail, explaining the slightly lower framerate.
Volumetric Lighting
Volumetric Lighting affects the quality of light shafts, also known as God Rays, and the quality of effects passing through light shafts and bright light.
Below, you can see how the accuracy of light shafts increases in step with the detail level, and how darker voids in light shafts become more defined, improving the efficacy of the effect:
| Interactive Comparisons | ||
| High vs. Medium | High vs. Low | Medium vs. Low |
Subtle light shaft variations aside, in-game you will instantly notice the impact of lower detail levels on visual effects. In the example below, the edges of the effect become increasingly aliased, flicker, and generally suffer from temporal instability and artifacting.
These issues occur across the entire surface of the effect, but are most prominent where you can see differences in quality in our static shots. Furthermore, quality scales with resolution, meaning 1920x1080 Low will look significantly worse than 2560x1440 Low. We would therefore recommend Medium or High for just about everyone.
| Interactive Comparisons | ||
| High vs. Medium | High vs. Low | Medium vs. Low |
Across wider shots, quality variations are harder to observe, though in-game, with effects billowing and moving, a keen eye will quickly notice that's something not quite right on Low.
| Interactive Comparisons | ||
| High vs. Medium | High vs. Low | Medium vs. Low |
Performance: Amping up the sample counts, resolution and quality of each Volumetric Lighting effect can decrease framerates by 11 frames per second.
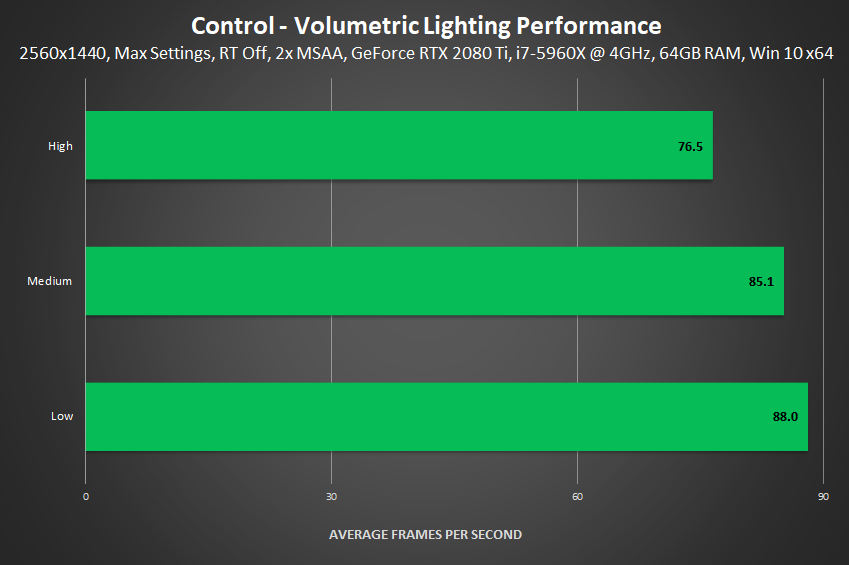
For optimum performance, we recommend first trying Medium - if you don't notice, or don't care about its reduced quality, your framerate will be a whole lot higher.
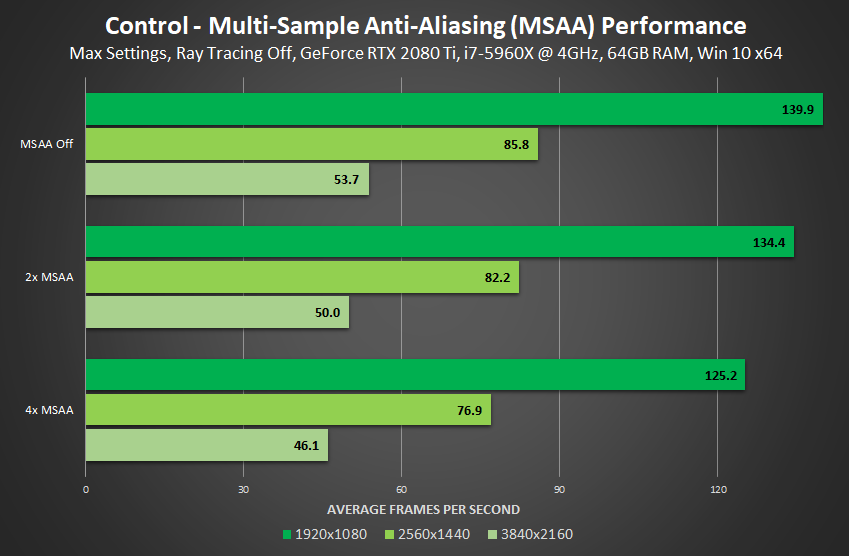
NVIDIA DLSS, MSAA and Other Anti-Aliasing
Control's look is intentionally filmic, with soft, lifelike visuals, minimizing the benefit of anti-aliasing.
Nevertheless, Control does include a Multi-Sample Anti-Aliasing (MSAA) option for those wanting to zap any outstanding jaggies, along with several other options for scaling and adjusting the rendering resolution.
Starting with MSAA, in the example below you'll struggle to find aliased edges, even with MSAA switched off. Zooming in, look at the back of the chair by the edge of the carpet, and the black divider between the carpet and glossy floor.
| Interactive Comparisons | ||
| 4x MSAA vs. 2x MSAA | 4x MSAA vs. MSAA Off | 2x MSAA vs. MSAA Off |
Thanks to post effects and other screen treatments, aliasing is greatly reduced at all resolutions, and what remains rarely looks like a sawtooth edge, as you'd typically find in other titles, hence the reduced benefit of MSAA.
Additional tests also reveal that alpha textures with transparency, as used for foliage and the protagonist's hair, are improved by MSAA, suggesting the inclusion of Alpha To Coverage or some other transparency anti-aliasing effect (a standard implementation of MSAA can only anti-alias geometry edges).
| Interactive Comparisons | ||
| 4x MSAA vs. 2x MSAA | 4x MSAA vs. MSAA Off | 2x MSAA vs. MSAA Off |
And wrapping up this unusual implementation of MSAA is the fact that it runs significantly faster than any other use of MSAA we've ever seen:
But despite this accelerated performance, you may find your framerate lower than you like. To help, Control includes robust resolution scaling options, as well as NVIDIA DLSS for GeForce RTX users. Using either of these techniques, players can decrease the graphics rendering resolution to accelerate framerates, while continuing to render the game's UI at their native screen resolution.
With the in-game "Render Resolution" option, that we refer to as Render or Resolution Scaling, you can select resolutions down to 1280x720 on a 16:9 monitor, and subsequently apply MSAA to smooth aliasing on the now-upscaled graphics.
To provide extra flexibility, NVIDIA DLSS in Control includes a new option that allows users to select the underlying target render resolution -- effectively a DLSS quality knob. Upon selecting NVIDIA DLSS, users can choose from one of two Render Resolutions. The lower of the two provides the biggest performance boost, while the other emphasizes higher image quality. This flexibility allows gamers to tune to their preferred experience.
On a 16:9 monitor, the available DLSS options at each resolution are:
- 3840x2160: Scale to 2560x1440 or 1920x1080
- 2560x1440: Scale to 1706x960 or 1280x720
- 1920x1080: Scale to 1280x720 or 960x540
Below, we compare DLSS to many other MSAA and Resolution Scaling configurations at all three resolutions. In general, we found that in static images NVIDIA DLSS delivers a noticeably clearer picture that retains more detail. For examples, take a look at these 2560x1440, 1920x1080 and 1706x960 comparisons.
And in-game, we see fewer upscale artifacts when the player or camera is moving, increasing clarity, fidelity, and detail, for a better gaming experience.
With DLSS enabled in situations where the GPU is under heavy load, framerates can increase by as much as 89% using the higher-fidelity mode, and up to 197% when using lower resolution performance modes.
Below, we chart performance across our entire lineup of GeForce RTX GPUs using NVIDIA DLSS's high-fidelity mode, with every ray tracing effect enabled, and other graphics settings maxed out.
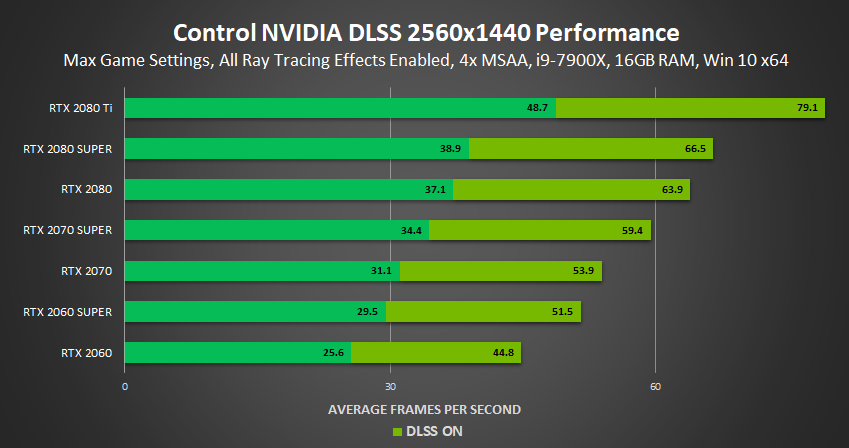
At 1920x1080, performance becomes CPU bottlenecked at around 80 FPS
In conclusion, we've demonstrated that NVIDIA DLSS delivers higher visual fidelity than traditional resolution upscaling, and greatly improves performance, too. If, however, you're chasing the highest possible framerates and don't mind lower levels of image quality, Resolution Scaling can further accelerate framerates:
If any of the resolution and anti-aliasing configs fail to float your boat, consider experimenting with injectable post-process anti-aliasing and/or sharpening via NVIDIA Freestyle or ReShade. And try creating a NVIDIA Control Panel custom resolution that gives you the exact level of performance you desire.
Next-Level Realism and Fidelity With Multiple Ray-Traced Effects
Before we bring things to a close, we wanted to demonstrate how the various ray-traced effects come together to collectively improve scenes. In the thumbnails below, you can follow the evolution of a scene, starting with max settings and ray tracing off. In sequence, we then enable Ray-Traced Reflections, followed by Ray-Traced Transparent Reflections, Ray-Traced Indirect Diffuse Lighting, and finally, Ray-Traced Contact Shadows.
At each stage, entire sections of each scene are improved, and often they further improve the fidelity, accuracy and realism of previously-enabled effects.
Offering unprecedented realism and detail, ray-traced effects are poised to deliver the biggest leap in image quality and immersion in decades.
When testing the ray-traced effects in isolation earlier in our guide, you'll have seen noticeable reductions to framerates in each benchmark. But together, because rays are already being fired and traced throughout a scene, the cost of adding a new effect is often far lower.
In our final set of charts, we're measuring this by recording the total combined framerate when each effect is enabled in turn, as in our screenshots above. So for example, enabling Contact Shadows takes the framerate from 120 to 110, and adding Indirect Diffuse Lighting lowers it to 90. Then, come the very end, when everything's enabled, the in-game framerate's 62.
With both Ray-Traced Reflections and Ray-Traced Transparent Reflections only requiring short additional ray bounces, and rays already being traced by other effects, framerates decrease by just an extra few frames per second when they're enabled, even at 4K. In isolation though, with no other effects enabled, their framerate costs are as-described earlier in our guide
Settings Wrap-Up
Many of Control's effects and features are baked-in, giving gamers limited options for improving performance, without decreasing image quality to a particularly noticeable extent. If you do need to improve things, however, here are a few nips and tucks to consider:
- Global Reflections: Medium instead of High: ~+2 FPS
- MSAA: 2x instead of 4x: +2-4 FPS (or try injecting fast post-process anti-aliasing)
- Screen Space Reflections: Medium instead of High: +9 FPS (if Ray-Traced Reflections is Off)
- Texture Resolution: High instead of Ultra: ~+2 FPS
- Volumetric Lighting: Medium instead of High: +9-11 FPS
GeForce Experience: Optimal Playable Settings With A Single Click
If you don't wish to manually adjust settings, the best way to automatically configure Control for a smooth, enjoyable experience is through GeForce Experience, an invaluable tool for all GeForce users. And in addition to optimizing over 600 games, the free GeForce Experience application can automatically update drivers and profiles, and record and stream gameplay with ShadowPlay.
Taking into account your GPU and CPU, as well as many additional factors, GeForce Experience's game recommendations can be applied with a single click and are updated over time should developer patches and NVIDIA driver updates improve performance further still. This one-click solution is perfect for gamers who wish to simply play their games, and for those with little experience in configuring settings for an optimal experience.
Game Ready Control Driver
For the best Control experience we recommend updating your system with the Control GeForce Game Ready Driver. This includes day-1 optimizations and fixes, and will ensure the best possible experience from the second you start playing. To download, head to the Drivers tab in GeForce Experience, or download manually from our website.
The Definitive Control Experience
Control raises the bar for realism, immersion, image quality, and graphical fidelity. By marrying lifelike real-time ray-traced effects with cinematic visuals, previously impossible sights are seen for the very first time.
Before now, these were simply impossible to render, but with ray tracing, lifelike visuals finally become a reality.
To see them in action for yourself, pick up a copy of Control with the purchase of a GPU, desktop or laptop participating in our current bundle, or if you already have a GeForce RTX system, head here. But before you play, be sure to download and install the aforementioned Control Game Ready Driver for the best possible day-1 performance.