Offload CPU usage to enhance user experience on modern applications and improve user density—cost-effectively meeting the needs of dynamic workloads.
Improved User Density and TCO
Powering Compute-intensive Workloads
Support a diverse array of workloads, ranging from daily business operational applications to AI, in a unified, virtualized environment.
GPU Sharing and Utilization
Divide GPU resources and share them across multiple virtual machines (VMs), or allocate multiple GPUs to a single VM to power the most demanding workloads.
Enterprise-Grade Software
Continue to optimize your ROI and deliver enhanced enterprise features, security, and support through consistent software releases.
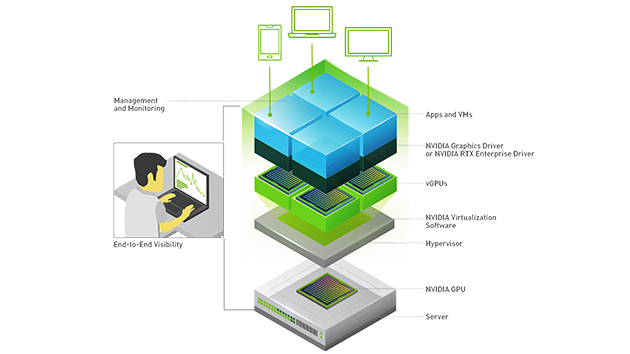
Take a Peek Under the Hood
In an NVIDIA vGPU-powered virtualized environment, the vGPU software, installed at the virtualization layer with the hypervisor, creates virtual GPUs that enable one physical GPU to be shared with multiple VMs or one single VM to harness the power of multiple physical GPUs.
vGPU software includes a graphics or enterprise driver for every VM. Since work that was typically done by the CPU is offloaded to the GPU, the user has a much better experience. This enables support for demanding engineering and creative applications, as well as compute-intensive workloads like AI and data science, in a virtualized and cloud environment.
How to Deploy NVIDIA vGPU
Start here for guidance on how to get started with NVIDIA vGPU technology, access tips and best practices for sizing your environment, or contact NVIDIA Enterprise Support.
- Tech Tips
- Documentation and Resources
- License and Support
vGPU Tech Tips Playlist
Find technical “how to” videos to help you get started on your vGPU journey. View our playlist of introductory videos, installation walk-throughs, and tips for success.

vGPU Technical Documentation and Resources Hubs
Learn how to deploy NVIDIA vGPU with your hypervisor of choice. Find best practices for sizing the vGPU deployment for the applications your users need daily, or determine which NVIDIA GPU is best suited for your workload with our technical documentation.
vGPU License and Support Portal
Manage your vGPU software licenses and contact NVIDIA enterprise support. NVIDIA support services for vGPU software provide access to comprehensive software patches, updates, upgrades, and technical support. Our support portal is an easy, reliable way to access personalized, proactive support.
Read the latest news and customer stories.

Advance Workstyle Reform
“We had a telecommuting system in place, but CAD work could not be done without coming into the office, so designers were unable to use it. With the introduction of NVIDIA RTX vWS, we are no longer restricted to coming into work, and are able to schedule our day more freely.”
- Kazutaka Shimizu, Assistant Manager of ZEV B&D Lab, Toyota Motors Corporation

Connect Anytime, Anywhere
“One of our biggest challenges in the centre is space, which is limited in terms of health and safety regulations. The new system allows more staff to work offsite, which means we have more space available for patients.”
- Dr. Subhadip Ghosh-Ray, Consultant Head and Neck Radiologist, Lead Consultant for Information Technology, PSSC

Quickly Deploy New PCs
“...I was able to quickly prepare and provide the environment for about 50 virtual PCs.”
- Sho Wakamatsu, VDI Team Sub-Leader, Information System Department, Square Enix

Limitless Learning
“Without the NVIDIA GPUs, we could not run our demanding workloads or offer the classes for which they are crucial.”
- Julian Erber, DevOps Manager, Parkway School District
NVIDIA vGPU Ecosystem Partners
Leverage familiar tools and choose from an ecosystem of partner solutions that offer single-pane-of-glass management of the virtualized infrastructure—from the client to the server to the GPU and beyond.
- Virtualization
- CSPs
- Servers
NVIDIA vGPU is supported with all major hypervisors to deliver accelerated compute and visually rich user experiences to virtualized environments that simplify management and increase flexibility, while maintaining data security.
Spin up a new virtual workstation in minutes, with access to NVIDIA GPU-accelerated instances from our cloud service provider partners.
The NVIDIA vGPU solution is available from the top OEM server vendors and through the NVIDIA Partner Network.
View the NVIDIA vGPU certified server list for full details on which OEM servers support which NVIDIA GPUs, along with the GPU density per server.
How to buy.
Purchase the NVIDIA vGPU solution from an NVIDIA Partner Network partner. Our extensive network of trained partners can help with architecting and deploying an optimal, accelerated virtualized environment.
Explore Virtual GPU Software Solutions

NVIDIA RTX Virtual Workstation (vWS)
Virtual Workstations for creative and technical professionals using graphics applications.

NVIDIA Virtual PC (vPC)
Virtual desktop infrastructure for knowledge workers who use office productivity applications and multimedia.

NVIDIA Virtual Applications (vApps)
Application streaming with Remote Desktop Session Host solutions.